Schema Registry Serialize/Deserialize (SERDES)
5 Minute Read
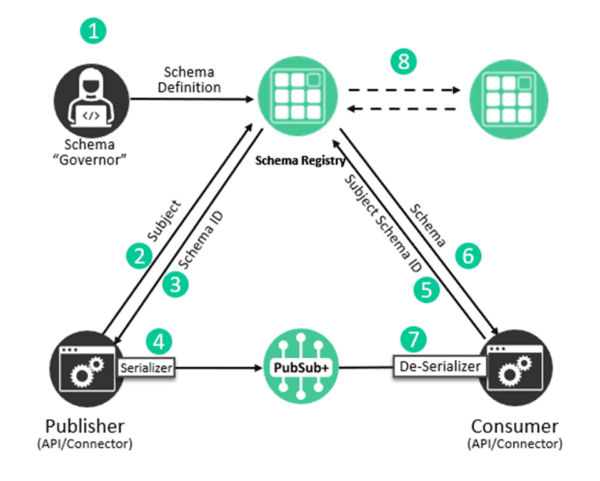
This feature exploration shows how to use the Solace Schema Registry with JSON Schema serializers and deserializers (SERDES) to automatically validate and manage event schemas when publishing and consuming events. AVRO and generic SERDES are also available in JCSMP and work in a very similar way. We will not explore those examples specifically in this tutorial but there are samples available in the JCSMP Samples repository.
Feature Overview
The Solace Schema Registry provides a centralized repository for managing message schemas, enabling schema validation, versioning, and evolution across your event-driven applications. The Schema Registry SERDES integration with JCSMP allows you to serialize and deserialize messages while automatically validating them against registered schemas.
Key benefits include:
- Automatic Schema Validation: Messages are validated against registered schemas during serialization and deserialization
- Type Safety: Serialize from and deserialize to Plain Old Java Objects (POJOs) with compile-time type checking
- Schema Evolution: Manage schema versions and support backward/forward compatibility
- Centralized Management: Store and manage schemas in a centralized registry accessible by all applications
The Schema Registry SERDES library supports both JSON Schema and Apache Avro formats. This tutorial focuses on JSON Schema serialization and deserialization, but Avro support is also available in the sample repository. For generic serialization and deserialization examples, see the complete sample code in the GitHub repository.
Prerequisites
- A Solace Event Broker (version 10.5 or later) with Schema Registry deployed
- Access to the Schema Registry with appropriate credentials
- JSON Schema files uploaded to the Schema Registry
- There must be a suitable Client Profile configured on your broker
For guidance on schema registry setup complete the Schema registry codelab
For more information about the Solace Schema Registry, refer to the Schema Registry Overview documentation.
NOTE: The Schema Registry SERDES library requires the following Gradle dependencies:
implementation(platform('com.solace:solace-schema-registry-serdes-bom:1.+'))
implementation 'com.solace:solace-schema-registry-jsonschema-serde'Configuring the Schema Registry Connection
Before using the serializers and deserializers, you need to configure the connection to the Schema Registry. The configuration uses environment variables or system properties:
/**
* Returns a configuration map for the Json Schema serializer.
*
* @return A Map containing configuration properties
*/
private static Map<String, Object> getConfig() {
Map<String, Object> config = new HashMap<>();
config.put(SchemaResolverProperties.REGISTRY_URL, REGISTRY_URL);
config.put(SchemaResolverProperties.AUTH_USERNAME, REGISTRY_USERNAME);
config.put(SchemaResolverProperties.AUTH_PASSWORD, REGISTRY_PASSWORD);
return config;
}JSON Schema Serialization
To serialize messages using JSON Schema, create a JsonSchemaSerializer and configure it with your Schema Registry connection details. The serializer validates your Java objects against the registered schema before converting them to JSON.
Creating and Configuring the Serializer
// Create and configure Json Schema serializer
try (Serializer<User> serializer = new JsonSchemaSerializer<>()) {
serializer.configure(getConfig());
// Create a JCSMP session and set up the topic
JCSMPSession session = createSession(host, vpn, clientUsername, password);
Topic topic = JCSMPFactory.onlyInstance().createTopic(TOPIC);
// Create a message producer
XMLMessageProducer producer = createProducer(session);
// Create and populate a User object with sample data
User user = new User();
user.setName("John Doe");
user.setId("-1");
user.setEmail("support@solace.com");
BytesMessage msg = JCSMPFactory.onlyInstance().createMessage(BytesMessage.class);
WaitForEnterThread exitListener = new WaitForEnterThread();
exitListener.start();
int index = 0;
while (!exitListener.isDone()) {
//update message
user.setId(String.format("%d", index));
try {
// serialize and send the message
SerdeMessage.serialize(serializer, topic, msg, user);
producer.send(msg, topic);
System.out.printf("Sending Message: %s%n", user);
} catch (JsonSchemaValidationException ve) {
// Handle cases where the message fails validation against the schema.
// This could happen if the schema in the registry is different from what is expected.
System.out.println("Validation error: " + ve.getMessage());
}
index++;
Thread.sleep(100); //limit send rate
}
exitListener.join();
session.closeSession();
}If the data doesn't conform to the registered schema, a JsonSchemaValidationException will be thrown during serialization.
JSON Schema Deserialization
Deserialization works in reverse - it validates incoming JSON messages against the registered schema and converts them to Java objects.
Deserializing to JsonNode
For flexible JSON handling, you can deserialize to Jackson's JsonNode:
// Create and configure Json Schema deserializer
try (Deserializer<JsonNode> deserializer = new JsonSchemaDeserializer<>()) {
deserializer.configure(getConfig());
// Create a JCSMP session and set up the topic
JCSMPSession session = createSession(host, vpn, clientUsername, password);
Topic topic = JCSMPFactory.onlyInstance().createTopic(TOPIC);
// Create a message consumer and subscribe to the topic
final XMLMessageConsumer consumer = session.getMessageConsumer((XMLMessageListener) null);
session.addSubscription(topic);
WaitForEnterThread exitListener = new WaitForEnterThread();
exitListener.start();
// Start the consumer and wait for a message
consumer.start();
while (!exitListener.isDone()) {
// Try to receive a message with a 1-second timeout
BytesXMLMessage msg = consumer.receive(1000);
if (msg == null) continue;
try {
// Deserialize the received message
// Note: The deserializer will return a generic JsonNode unless a target POJO is specified.
// There are two ways to specify the target class:
// 1. In the deserializer configuration: Set the SerdeProperties.DESERIALIZED_TYPE property.
// 2. In the schema: Add a property that contains the fully qualified Java class name.
// - The name of this schema property is determined by JsonSchemaProperties.TYPE_PROPERTY.
// - By default, its value is "javaType". For example: { "javaType": "com.my.User" }
// - You can configure TYPE_PROPERTY to use a different key if your schemas follow another convention.
JsonNode jsonNode = SerdeMessage.deserialize(deserializer, msg);
System.out.println("Got message: " + jsonNode);
} catch (JsonSchemaValidationException ve) {
System.out.printf("Received Message with invalid payload:%nValidation error: %s%n", ve);
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
System.out.printf("Received Message with payload that can not be decoded:%nDecoding error: %s%n", re);
}
}
exitListener.join();
session.closeSession();
}Deserializing to POJOs
For type-safe deserialization directly to Java objects, configure your JSON Schema with the customJavaType property. This allows the deserializer to automatically map JSON to your POJO:
// Create and configure Json Schema deserializer
try (Deserializer<User> deserializer = new JsonSchemaDeserializer<>()) {
deserializer.configure(getConfig());
// Create a JCSMP session and set up the topic
JCSMPSession session = createSession(host, vpn, clientUsername, password);
Topic topic = JCSMPFactory.onlyInstance().createTopic(TOPIC);
// Create a message consumer and subscribe to the topic
final XMLMessageConsumer consumer = session.getMessageConsumer((XMLMessageListener) null);
session.addSubscription(topic);
WaitForEnterThread exitListener = new WaitForEnterThread();
exitListener.start();
// Start the consumer and wait for a message
consumer.start();
while (!exitListener.isDone()) {
// Try to receive a message with a 1-second timeout
BytesXMLMessage msg = consumer.receive(1000);
if (msg == null) continue;
try {
// Deserialize the received message
// Note: the 'customJavaType' property in the schema specifies the 'User' class, so the deserializer returns a User object.
User user = SerdeMessage.deserialize(deserializer, msg);
System.out.println("Got message: " + user);
} catch (JsonSchemaValidationException ve) {
System.out.printf("Received Message with invalid payload:%nValidation error: %s%n", ve);
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
System.out.printf("Received Message with payload that can not be decoded:%nDecoding error: %s%n", re);
}
}
exitListener.join();
session.closeSession();
}Error Handling
When working with Schema Registry SERDES, handle these common exceptions:
- JsonSchemaValidationException: Thrown when data doesn't conform to the registered schema
- RuntimeException: May be thrown for deserialization errors or encoding issues
- JCSMPException: Standard JCSMP exceptions for connection and messaging issues
try {
byte[] data = serializer.serialize(topic, payload);
} catch (JsonSchemaValidationException e) {
System.err.println("Validation error: " + e.getMessage());
// Handle invalid data - fix schema or data
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Serialization error: " + e.getMessage());
// Handle other serialization issues
}Additional SERDES Support
This tutorial demonstrates JSON Schema serialization and deserialization. The Solace Schema Registry SERDES library also provides:
- Apache Avro SERDES: For binary serialization with Avro schemas
- Generic Serializers/Deserializers: For working with multiple schema formats dynamically
For complete examples of these features, see the SERDES samples in the GitHub repository.